A version of this essay has been published by firstpost.com at https://www.firstpost.com/opinion/climate-tragedy-of-wayanad-and-the-vulnerability-of-western-ghats-13808331.html
Here’s a new AI-generated podcast courtesy of Google NotebookLM that summarizes this essay.
After days of intense coverage of the landslides in Wayanad, the news cycle has moved on to other calamities. But the problems remain, and things cannot be left to benign neglect as is usually the case. For example there was a strange thundering noise from deep underground that alarmed people in the area. This is ominous, as it may presage a tectonic movement, although there have been no big quakes here for centuries.
A dramatic before-and-after report from Reuters, using satellite images from Planet Labs, Google, Maxar Technologies and Airbus, shows how the landslide left a giant scar on the surface of the earth, washing away hundreds of houses, leading to widespread fatalities and destruction.
Prime Minister Modi visited the afflicted area. Better governance, both by Center and State, is sorely needed to tackle the problem, because it is not simple: there are proximate, preponderant and root causes. A lot of it is anthropogenic based on local factors, but climate change is also a major factor, as the local climate and rainfall patterns have shifted dramatically in the recent past. There was a drought in 2015, followed by the Ockhi cyclone in 2017, and then landslides and floods in 2018 and 2019.
As a resident of Kerala, who has visited Wayanad only twice (once in 2018 and the second time in April this year), both the problems and the possible solutions are of immediate importance to me, because the very same issues are likely to crop up all over the State, and unless remedial measures are taken now, we can expect further tragedies and endless suffering.
Proximate Cause: Excess Rain
The proximate cause is La Nina-enhanced rainfall, which has been higher this year along the west coast. In Wayanad itself, it rained 572mm in 48 hours before the landslide: about 1.8 feet, an enormous amount.
Before the Wayanad landslide, there had been another in Shirur on the Karnataka coast near Ankola, where a number of people were swept away. The story of Arjun, a Kerala trucker whose truck full of lumber disappeared, was all over the news, and after a weeks-long search, there was no sign of him or the truck.
The total rainfall since June 1 was of the order of 3000mm in Wayanad, which is unusually high, creating vulnerability to landslides. In a recent interview, environmental expert Madhav Gadgil mentioned that quarrying may have added to the intensity of the rainfall, because the fine dust from the mining and explosions forms aerosols, on which water molecules condense, leading to excessive precipitation.
The intense rainfall saturated the soil, and in the absence of sufficient old-growth vegetation that might have held it together, the hillside simply collapsed.
Preponderant Cause: Population Pressure, Over-Tourism, Ecocide
The preponderant causes of the problems in Wayanad are obvious: population pressure, over-tourism and environmental destruction. The forest has basically ceased to exist due to human exploitation. According to India Today, 62% of the green cover in the district disappeared between 1950 and 2018 while plantation cover rose by around 1,800%. Fully 85% of the total area of Wayanad was under forest cover until the 1950s.
Overpopulation, settlement and habitat loss
My first visit to Wayanad was in 2018, when we drove to Kerala from Karnataka: from the Nagarhole/Bandipur Wildlife Sanctuaries to the contiguous Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary, all forming a Project Tiger ecosphere along with neighboring Mudumalai Wildlife Sanctuary in Tamil Nadu. Together they form the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve.
Bandipur/Nagarhole actually looks like a forest. But I was astonished when we drove into Wayanad, because it does not look like a forest any more: it is full of human habitation. It looks like any of the other districts in Kerala: thickly populated, with settlements all over the place. It appeared to be only notionally a wildlife sanctuary.
Habitat loss, especially that of forest cover, is true of all of Kerala, as highlighted in a study by IISc scientists. It is startling to see how much of this has happened in just a few decades. But it is the culmination of a process that started at least a century ago.
Wayanad, according to myth and legend, was once a lovely, lush forest inhabited by a small number of tribals. There were fierce Kurichya archers (it is possible they were warriors banished to the forest after losing a war) who, with Pazhassi Raja, carried on a guerilla war against the British colonials in the 19th century until the Raja was captured and executed. I visited the Pazhassi Museum in Mananthavady this May, on my second visit to Wayanad. There were artifacts there from the tribal settlements.
Then, in the 20th century, there was a large migration of lowland people, mostly Christians from Central Travancore, to the Wayanad highlands (and the Western Ghats uplands in general). They encroached on public/forest lands, cleared the forests, and created plantations and agricultural settlements. Their struggles against malaria, wild animals and the land itself was the subject of Jnanpith winner S K Pottekkat’s renowned novel Vishakanyaka (Poison Maiden).
The public land thus captured eventually made some people rich, but the whole process also in effect enslaved the tribals, who became an exploited underclass: the very same story as of Native Americans, who are still struggling for social justice after centuries of being untermenschen.
Since most of the settlers were Christians, the Church became a powerful spokesman for them. Successive governments gave a lot of the settlers title to the land they had illegally captured. So there is a class of rich planters, and on the other hand, miserable plantation workers, often migrants especially from Tamil Nadu.
The green deserts need to be turned back into forests
Kerala’s highlands, over time, became ‘green deserts’, rather than ‘tropical rainforests’. The monoculture of tea, rubber, coffee, and especially invasive species such as acacia and eucalyptus is destructive. They crowd out native species, ravage the water table, do not put down deep roots, and offer almost no sustenance to wild animals. It may look deceptively green, but it is no forest.
An expert committee, the Madhav Gadgil Commission, recommended in 2011 that the entire Western Ghats was ecologically sensitive (ESA or Ecologically Sensitive Area) and 75% of it must be preserved intact with minimal human presence. The report was scathing about quarrying, including blasting with dynamite, which upset the already fragile ecosystem, ravaged as it was by the removal of old growth forest and the root system that held the soil together.
At the time, Gadgil did say that the calamity would not take a 100 years, but it would happen in ten to twenty years. He was right, but he was ignored as though he were Cassandra.
The Church opposed the Gadgil report tooth and nail, and the Government of Kerala pushed back on it. So the Central government created the Kasturirangan Commission (2013), which reduced the proposed ESA to 37%. It classified 60% of the Western Ghats as a ‘cultural landscape’ with human settlements, plantations and agriculture.
But that too was not acceptable. In fact, Jayanthi Natarajan claimed that she was forced to resign as Environment Minister because she actually notified the order on protection of the Western Ghats the day before she was removed. Her successor duly put the order on hold.
Sitting Congress MP in nearby Idukki, P T Thomas, says he was dropped in the 2014 elections because he supported the Gadgil report against “encroachments… illegal constructions, quarrying, timber smuggling, sand mining from the rivers and ganja cultivation…My stand upset the Idukki dioceses of the Syro Malabar Catholic Church. The Idukki Bishop had openly opposed my candidature.”
The GoK convened a third committee, the Oommen Commission (2014), which was specific to Kerala, and it recommended keeping all inhabited areas and plantations out of the ESA altogether. Mission accomplished. No more restrictions on land use.
Over-tourism and carrying capacity of the land
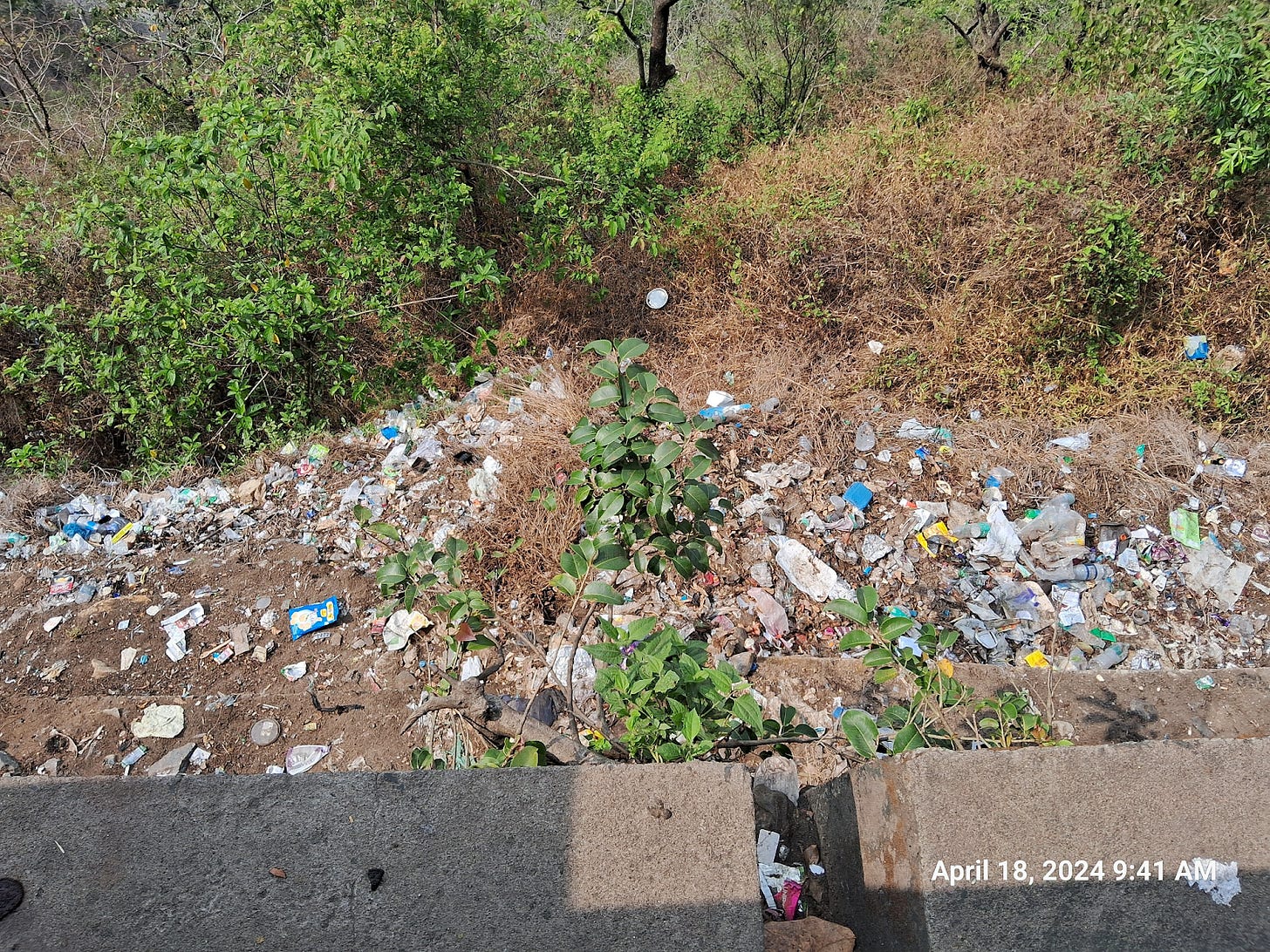
This is one reason for the proliferation of resorts and homestays in Wayanad. Every second house caters to tourists, as can be seen from a Google Map (of the area around Kalpetta). The environmental pressure from this (what about solid waste disposal? Do they dump liquid wastes into rivers?) is horrific and increasing. Trash lines the area near the Thamarassery Pass.
As a tourist myself, I did not choose a plantation resort, but instead a homestay which has a working farm. Perhaps I made a wrong choice, because a plantation has a lot of space to absorb the tourist impact. The homestay had many youngsters from Bangalore over the weekend, and it was perfectly nice, but I wonder how much I contributed to the human toll on the environment.
I had gone to Wayanad to visit the Thirunelli temple and the Edakkal caves, which have petroglyphs and drawings reliably dated back to 8000 Before the Present, making them second only to the Bhimbetka caves in Madhya Pradesh, whose rock art dates back to 10,000 BP and earlier. So this area, despite the geological fault lines, has indeed been inhabited for a very long time. The carrying capacity of the land was sufficient in those prehistoric times and even up until recently; now the land can no longer sustain the population.
It is also host to another recent influx. Muslims from nearby lowland Kozhikode and Malappuram districts have come up the Thamarassery Pass and settled in Wayanad in numbers. They have added to the population pressure in Wayanad. Incidentally this is one reason Wayanad Lok Sabha constituency (which includes areas from nearby Kozhikode and Malappuram districts that are heavily Muslim) is so dependably a Congress citadel.
When I made my trip in April, just before elections, I asked several people who would win there: the candidates were Rahul Gandhi (Congress), Annie Raja (CPI), K Surendran (BJP). All of them said “Rahul Gandhi”. One man told me “Rahul Gandhi is going to become the PM”. Another laughed and said, “Are you joking? We all know the answer”. It was, pun intended, a landslide win for the Congress candidate.
Root Cause: Geology and Errant Rainfall
The root cause of the problems in Kerala is the increasingly unstable landscape. It is remarkable that Kerala has such a high number of landslides and vulnerable spots. India Today reports that Kerala has recorded the largest number of landslides in the country, 2,239 out of 3,782 that occurred between 2015 and 2022. The “Landslide Atlas of India 2023” from ISRO lists 13 out of 14 Kerala districts among the top 50 landslide-prone areas of the country.
This is surprising, because the more obvious fault lines must be in the North, where the Indian Plate continues to grind up against the Eurasian Plate, and the Himalayas and the Tibetan Plateau continue to gain a few centimeters in elevation every year. Indeed Arunachal, Himachal, J&K and Uttarakhand are landslide-prone. But why Kerala, at the other end of the land-mass?
It must be the case that there have been severe tectonic movements in Kerala in the past: the Parasurama legend of the land coming up from the sea is based on a real event, presumably caused by an earthquake in a prehistoric time frame. More recently, the thriving Kerala port of Kodungalloor (aka Muziris), the principal West Coast port in historical times along with Bharuccha in Gujarat, was suddenly rendered bereft in 1341 CE after a severe flood in the River Periyar, and port activities shifted to nearby Kochi.
More recently, old-timers talk about the Great Flood of ‘99, i.e. 1099 Malabar Era, or 1924 CE. Exactly 100 years ago there were torrential rains in July, and records suggest it was 3368mm or 1326 inches over three weeks, that is 11 feet of rain. Floodwaters rose up to 6 feet, rivers changed course, and at least 1,000 people died along with large numbers of livestock, and there was massive destruction of agricultural land and foodgrains. The Flood of ‘99 became etched in the collective memory of the area, but it mostly affected the lowland areas of Travancore and Cochin, leaving the highlands largely untouched.
That has changed with deforestation, quarrying, construction, and denudation of hillsides.
There were the floods of 2018, which affected the hills, especially in Munnar. A full mountainside fell 300 meters into a river there. Entire settlements were washed away. A total of 2,346mm of rain or 923 inches was recorded in July and August, almost 50% higher than the norm. 483 people were killed, with many more missing and unaccounted for. Infrastructure was wiped out, including roads and clean water supply. Dams had to be opened, wreaking havoc on those downstream.
There is also the perennial threat of Mullaperiyar Dam overflowing or being breached, which is, among other things, a source of friction between Kerala and Tamil Nadu.
Other root causes include the following:
Climate Change: A study by the World Weather Attribution group indicated that climate change has intensified rainfall in the region by about 10%, contributing significantly to the severity of the disaster. The ongoing increase in global temperatures has led to more extreme weather patterns, including heavier monsoon rains.
Soil Characteristics: Wayanad's soils are loose and erodible, particularly in areas with steep gradients exceeding 20 degrees. When saturated, these soils lose their structural integrity, making them susceptible to landslides. The presence of large boulders and mud further complicates the stability of the slopes during heavy rains.
Soil piping: Previous landslides in the region, such as the 2019 Puthumala event, created conditions for soil piping, where voids form in the subsurface soil, increasing the risk of subsequent landslides during heavy rainfall.
Lack of Effective Land Management Policies: There is a notable absence of comprehensive land use and disaster management policies in Kerala, particularly in ecologically fragile areas. Despite previous disasters, there has been insufficient progress in implementing hazard mapping and community awareness programs to mitigate risks associated with landslides.
Thus Kerala is vulnerable to a host of issues, especially climate change (which is also eating away at the coastline). Behind the tropical paradise facade of “God’s Own Country”, there lie tremendous dangers related to excessive human exploitation, amounting to ecocide. What is the solution?
Maybe Madhav Gadgil was right, after all, and strict controls should be imposed on human activity, especially denudation of forest, and quarrying. His report had included Vythiri, Mananthavady and Sulthanbathery taluks in Wayanad as Ecologically Sensitive Zone ESZ-1, which means no change whatsoever in land use is permissible there. Chooralmala, Mundakkai, and Meppadi, where the worst of the disasters happened, are all in Vythiri taluk.
No effective disaster prevention or mitigation efforts have been put in place. The only solution is reforesting and restoring green cover, and stopping construction, quarrying, and tourism and the most contentious issue, relocating people away from the ESZ. Unfortunately the tropical rainforest may not restore itself if simply left alone (as temperate-zone forests do), and perhaps efforts such as Miyawaki foresting with native species may need to be pursued.
It is to be hoped that we have not passed the point of no return. Kerala’s population is shrinking (Total Fertility Rate is 1.80, well below the replacement rate of 2.1 children per woman), but there is no limit to human greed.
What needs to be done
There are no magic solutions, but comprehensive climate action and improved disaster management strategies can mitigate things to an extent. Experts emphasize the importance of:
Enhanced Communication and Coordination: There is a critical need for better intergovernmental communication regarding disaster preparedness. This includes timely warnings and efficient evacuation plans to mitigate the impact of natural disasters.
Land Use Policies: Implementing stringent land use regulations is essential to prevent construction in ecologically sensitive areas. The degradation of green cover due to unregulated development has significantly increased the risk of landslides.
Early Warning Systems: Developing robust early warning systems for landslides and floods can provide crucial alerts to communities at risk. These systems should be supported by regular community education and drills to ensure residents are prepared for emergencies.
Afforestation and Environmental Conservation: Massive afforestation and reforestation drives (especially with native species) are necessary to stabilize hillsides and reduce landslide risks. Protecting and restoring natural habitats can help mitigate the effects of climate change and enhance biodiversity. Collaborating with local communities for reforestation projects can also provide economic incentives and foster a sense of stewardship.
Community Engagement: Empowering local communities to participate in disaster preparedness and environmental conservation efforts is vital. Education on risks and proactive measures can significantly reduce the impact of disasters.
Tourism Management: Over-tourism can exacerbate environmental degradation. Developing a sustainable tourism strategy that limits visitor numbers, promotes eco-friendly practices, and educates tourists about environmental conservation is essential. Establishing eco-tourism zones and supporting community-based tourism initiatives can provide economic benefits while preserving the natural environment.
Regulation of Quarrying and Construction: Strict regulation and monitoring of quarrying and construction activities are necessary to prevent ecological damage. Implementing sustainable practices in these industries, such as controlled quarrying methods and responsible waste management, can mitigate their impact on the environment. Regular audits and penalties for non-compliance can enforce these regulations.
Surveillance and meteorological data collection: With modern technology like drones, continuous monitoring of the landscape is possible at a relatively low cost; and this can also be used for collecting large amounts of meteorological data to support early-warning systems. Satellite images from India’s own as well as foreign sources can be used to warn of dangerous construction, quarrying, and loss of forest cover.
Some of these are purely technical solutions, offering computerized forecasts and disaster warnings. The social and governance aspects are even more important: discipline, co-operation and awareness on the part of the residents, and the strict enforcement of land use rules and regulations.
Dealing with powerful settlers, encroachers, and vested interests requires a delicate balance of enforcement and negotiation, carrot and stick. Government agencies, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), and local communities must collaborate to develop and implement policies that address these challenges. Advocacy for stronger environmental laws and community involvement in decision-making processes can help align interests and foster co-operation.
With all these in place, it may be possible to repair the damaged hills of the Western Ghats, one of the global hotspots of biodiversity.
2200 words, Aug 17, 2024 updated 3000 words, Aug 19